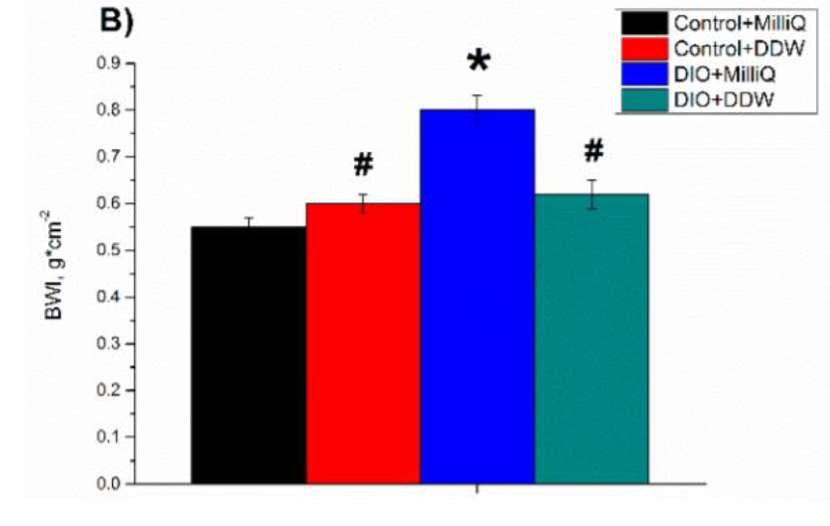
Preventa 45 deuterium-depleted drinking water (18 liters)
Preventa 45 deuterium-depleted drinking water (18 liters) Black is backordered and will ship as soon as it is back in stock.
Attachment
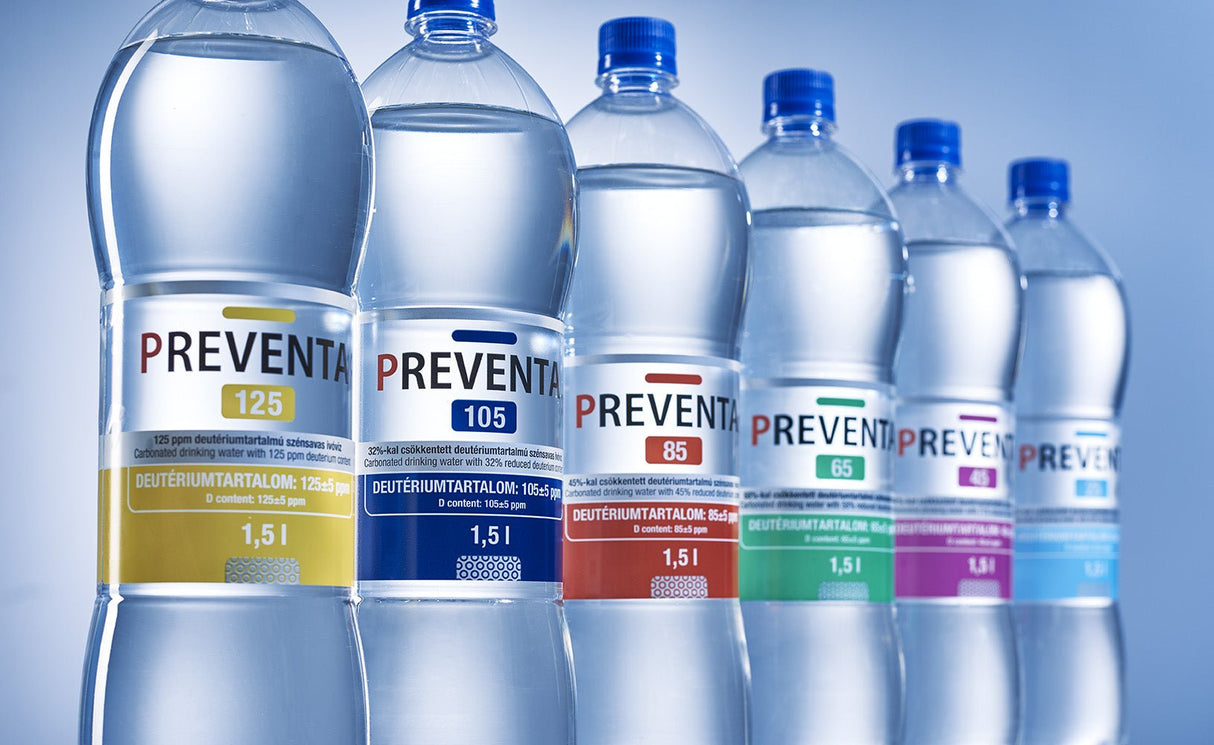
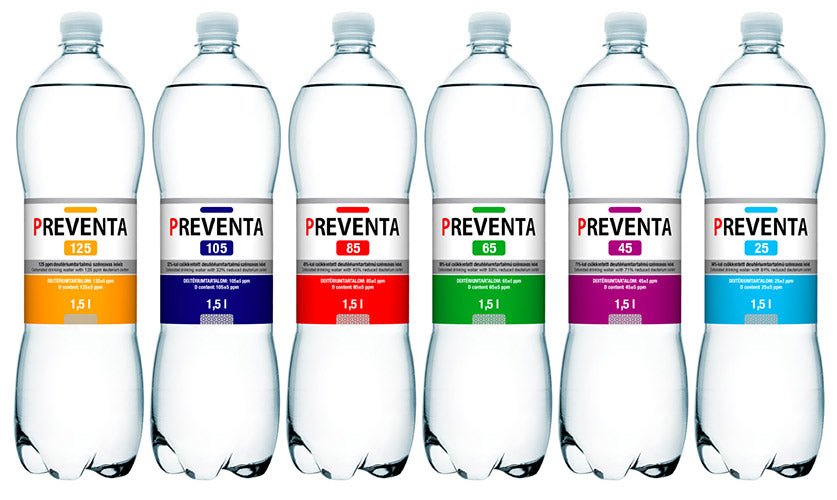
Preventa 45 deuterium-reduced drinking water (6 x 2 = 12 bottles = 18 litres)
Summary
Preventa 45 is an advanced deuterium-reduced drinking water with documented quality and a precise deuterium concentration of 45 ppm, developed to support the body's natural processes. The water is produced by HYD LLC., a pioneer in deuterium research and cancer biology, and is the result of over 20 years of scientific work and clinical experience. Preventa is used today by health-conscious people and professional athletes in over 50 countries.
Health benefits
- Supports cellular function and energy production
By reducing the levels of deuterium in the body, the water can contribute to better mitochondrial function and energy balance.
- Improves physical performance and recovery
Clinical studies show that deuterium-reduced water can lead to improved endurance, faster recovery and increased oxygen utilization during physical activity.
- Contributes to reduced oxidative stress
Lower levels of deuterium in the body are associated with reduced production of reactive oxygen compounds and improved cell health.
- Supports the body's ability to repair DNA
Reduction of deuterium in the cells can promote normal processes of DNA synthesis and repair.
- Supports the immune system
Research suggests that deuterium reduction can enhance the body's immune response through improved cellular homeostasis.
- Supports anti-aging mechanisms
Deuterium-reduced water can support metabolic and mitochondrial processes that weaken with age, and contribute to the maintenance of the body's natural repair mechanisms.
- Improves metabolism and glucose regulation
Can promote fat burning and contribute to better regulation of blood sugar, especially in people with metabolic imbalances.
Technical specifications
- Deuterium content: 45 ppm (95 mg/l HDO)
- Bottle size: 1.5 litres
- Package contents: 12 bottles (18 litres)
- Mineral content: Low content of sodium, calcium and magnesium bicarbonate
- Production method: Cryogenic fractional distillation
- Manufacturer: HYD LLC., Hungary
- Area of use: As a replacement for daily fluid intake
Reservation
Allowed to be used by adults. All use of supplements is at your own risk and should be done in consultation with a doctor.
The recommended daily dose should not be exceeded.
The effect of this product may vary from person to person.
Dietary supplements should not replace a varied diet.
Should be kept out of the reach of children.
Uno Vita AS does not claim that the products we market can cure disease.
Disclaimer
Uno Vita increasingly uses artificial intelligence for analyses, summaries and design of articles. We do not accept responsibility for possible errors in texts, articles or descriptions due to human or computer technology (AI) errors, inaccuracies or missing information in scientific and medical studies. We encourage all readers to examine all information critically to ensure that the content is correct. Uno Vita does not claim medical effects of the products we sell, but we refer to publicly available research in accordance with the right to freedom of expression. The information on this website is for informational purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. The content must not be used as a basis for making diagnoses or choosing forms of treatment. All information and materials on this website are provided "as is" without any warranties, either expressed or implied, including, but not limited to, implied warranties of merchantability, fitness for a particular purpose or non-infringement. Uno Vita disclaims all responsibility for loss or damage that may arise as a result of the use of information or products from this website. We strongly recommend that you consult a qualified healthcare professional before starting any new treatment, dietary change or use of supplements. Any use of products or information from this website is at your own risk.
Freedom of expression and right to information
Uno Vita reserves the right to share publicly available research and information on health and wellness technologies, natural substances, vitamins and the like. We do this with reference to national and international laws on freedom of expression and belief, including:
• UN Universal Declaration of Human Rights (1948): Article 19
• The International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (1966): Article 19
• Section 100 of the Norwegian Constitution
• America's First Amendment
Uno Vita reserves the right to freedom of opinion and expression in line with these principles.
Scientific references
-
Boros LG et al. (2016). Deuterium Depletion as a Targeted Therapy in Oncology. Medical Hypotheses.
-
Somlyai G. (2001). The Biological Effects of Deuterium Depleted Water. Integrative Cancer Therapies.
-
Cong F. et al. (2013). Effects of Deuterium-Depleted Water on Tumor Proliferation. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
-
Boros LG et al. (2014). Deuterium Depletion Enhances Mitochondrial Function. Biochim Biophys Acta.
-
HYD LLC (2015). Clinical Applications of Deuterium-Depleted Water. Internal Report.
-
National Institute of Sports Medicine (2005). Athletic Performance and Deuterium Depletion.
-
EMA (2015). Deuterium-Depleted Water as API. Regulatory Summary.
-
Nagy G. (2012). Aging and Cancer in the Context of Deuterium. J Aging Res.
-
HYD LLC (2019). Advances in Deuterium Depletion Technology. R&D Summary.
-
Somlyai G. (2010). Therapeutic Potential of Deuterium Depletion. Cancer Res J.
-
Boros LG et al. (2020). Metabolic Targeting by Deuterium Depletion. Mol Cell Biochem.
-
Wang L. et al. (2021). Role of Hydrogen Isotopes in Cellular Biochemistry. Biol Chem.
-
Zhang Y. et al. (2019). Deuterium and Oxidative Stress. Free Radic Biol Med.
-
HYD Pharma (2022). Preventa Protocols and Clinical Practice. Clinical Bulletin.
-
Tretyakov AI. (2017). Heavy Water Effects on Enzyme Function. Biochemistry (Moscow).
-
Kiss T. et al. (2015). DNA Repair and Hydrogen Isotopes. J Mol Biol.
-
Barna B. et al. (2013). Immunomodulation by Deuterium Depletion. Immunol Lett.
-
Boros LG. (2020). Glucose Metabolism Shift Induced by Deuterium. J Physiol Biochem.
-
HYD LLC. (2018). Production Methodologies for DDW. Tech Documentation.
-
Somlyai G. et al. (2021). Long-Term Effects of Deuterium Reduction. Aging Cell.
-
HYD LLC. (2023). Deuterium Depletion in Preventive Medicine. White Paper.