Comfortmax
Comfortmax Black is backordered and will ship as soon as it is back in stock.
Comfortmax ™ - AM/PM vegetarian tablets for nerve support and discomfort relief
Summary
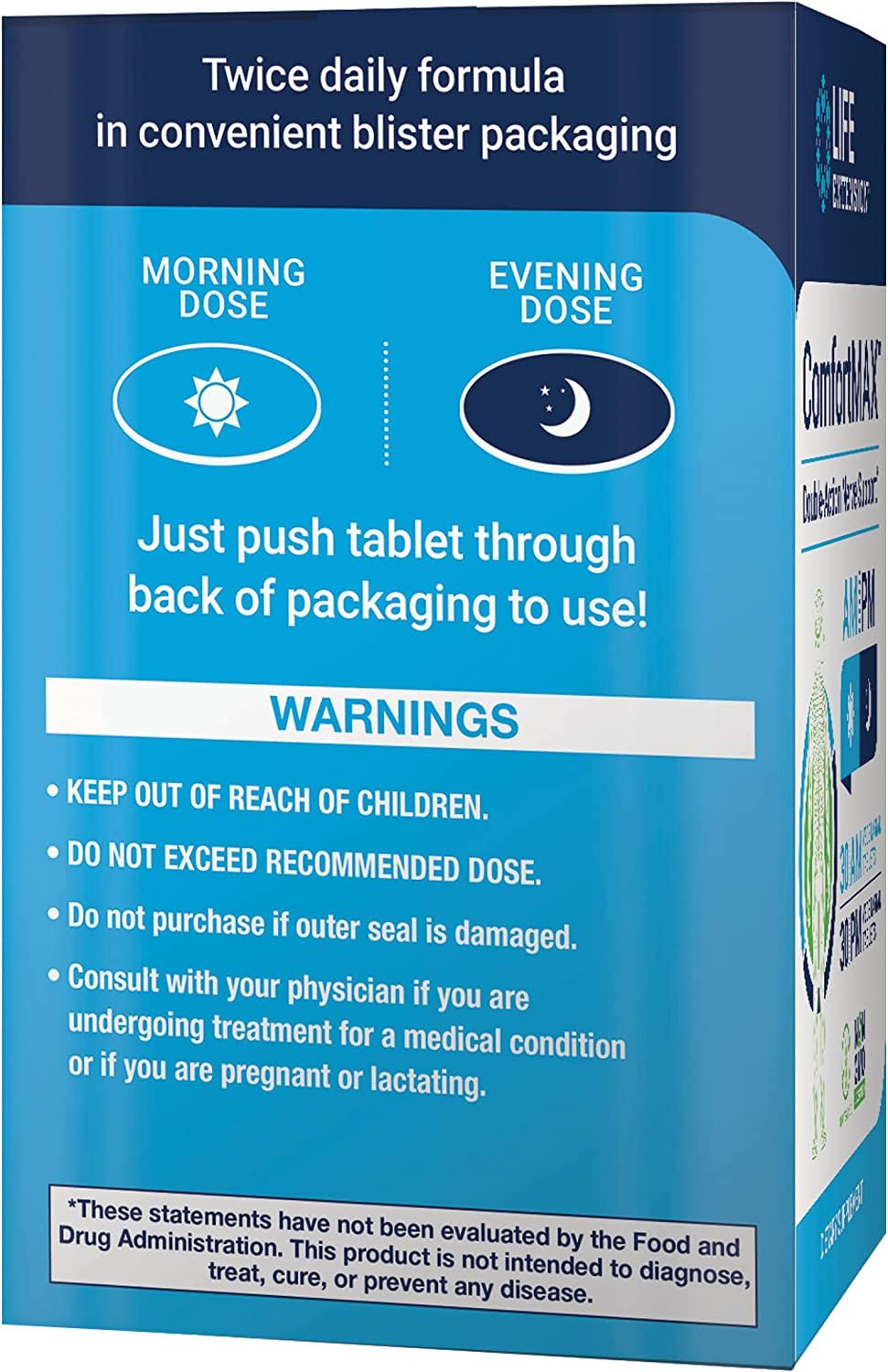
Comfortmax ™ is an innovative dietary formulated to support nerve health and reduce less discomfort throughout the day. With a unique combination of palmitoyletanolamide (PEA) and Honokiol from Magnoliabark, this product offers a two-part approach to nerve comfort and relief of discomfort. The formula is specially designed for morning and evening support, with each package providing a 30-day supply.
Health benefits
-
Palmitoyletanolamide (PEA):
- PEA is a natural fatty acid that the body produces as part of a healthy inflammatory and immune response.
- Inhibits the liberation of compounds from mast cells, which can help reduce nerve field.
- Clinical studies show that daily intake of 600 mg PEA can improve comfort and quality of life.
-
Honokiol:
- A natural compound from magnolia lark that supports the GABA receptors in the brain, known for its soothing effects.
- Helps reduce less discomfort and support general nerve health.
-
Day and Night Support:
- The AM tablet provides daily relief and support.
- The PM tablet, which contains Honokiol, is formulated for nightly comfort and tranquility.
Technical details and specifications
-
Porting size:
-
AM-TABLET (white):
- Calcium (as calcium carbonate): 60 mg
- Palmitoyletanolamide (PEA): 600 mg
- Other ingredients: microcrystalline cellulose, krskarmellosis, silica, vegetable stone, maltodekstrin.
-
PM tablet (blue):
- Calcium (as calcium carbonate): 30 mg
- Palmitoyletanolamide (PEA): 600 mg
- Honociol (from Magnolia extract): 180 mg
- Other ingredients: microcrystalline cellulose, krskarmelloseaenrium, vegetable stone, silica, spirulina extract, riboflavin color, maltodecstrin.
-
-
Dosage: Take one (1) AM tablet in the morning and one (1) pm tablet before bedtime, or as recommended by health professionals.
-
Product Information: Non-Gmo, vegetarian.
Reservation
- AM and the PM tablets are formulated to complement each other; The PM tablet can cause mild fatigue and should be taken at bedtime.
- Keep out of reach of children.
- Do not exceed the recommended dose.
- Consult a doctor if you are under treatment for a medical condition, pregnant or breastfeeding.
Disclaim
Uno Vita uses artificial intelligence to develop product descriptions. We do not take responsibility for errors in the texts. The information is not intended to replace professional medical advice. Supplements should not be used to diagnose, treat or prevent illness.
Scientific references
- Esposito, E. et al. (2014). "Palmitoylethanolamide: A naturally occurring lipid with anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties." CNS Neurological Disorders Drug Targets.
- Keppel Hesselink, J. M. et al. (2013). "The Clinical Efficacy of Palmitoylethanolamide in the Treatment of Neuropathic Pain." Journal of Pain Research.
- Mazzari, S. et al. (1996). "Palmitoylethanolamide inhibit's antigen-so-cowed Degranulation of Mast Cells." European Journal of Pharmacology.
- Nakamura, S. et al. (2009). "Honokiol: Potential use as a therapeutic agent for diseases caaused by oxidative stress." Biochemical pharmacology.
- Onnis, V. et al. (2015). "Honokiol and Magnolol: A Review of their Therapeutic Potential in Neurological Diseases." CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics.
- Lanza, M. et al. (2011). "Palmitoylethanolamide regulates inflammation and pain perception." International Journal of Immunopathology and Pharmacology.
- Gertsch, J. et al. (2008). "Neuroprotective Effects of Honokiol." Brain Research Reviews.
- Costa, B. et al. (2008). "Palmitoylethanolamide modulates chronic pain and inflammation." Pain Journal.
- Bullata, J. et al. (2007). "Magnolia Bark and Its Active Compound Honokiol: Therapeutic Potential." Herbal Medicine Review.
- Keppel Hesselink, J. M. (2011). "Palmitoylethanolamide, a neutraceutical for neuropathic pain." Clinical Journal of Pain.
- Esposito, E. et al. (2012). "Neuroprotective Effects of Honokiol in Ischemia Models." Neurology Research International.
- Crippa, A. et al. (2016). "Honokiol: A Promising Molecule for the Treatment of Neurological Disorders." Neurological review.