Vitamin B12 Methylcobalamin (1 mg)
Vitamin B12 Methylcobalamin (1 mg) Black is backordered and will ship as soon as it is back in stock.
Vitamin B12 Methylcobalamin (1 mg, 60 vegetarian soluble tablets)
Summary
Vitamin B12 Methylcobalamin is an essential nutrient that supports the body's energy production, nerve function and cellular health. Our vegetarian soluble tablets are formulated with methylcobalamin, the bioactive form of B12, and provide fast and efficient absorption in the body. This supplement is specially designed for people with reduced absorption of B12 through diet or the digestive system.
Benefits and effects
- Support for energy production: Vitamin B12 plays a central role in the conversion of food into energy, and helps to reduce fatigue and exhaustion.
- Neurological health: Supports healthy nerve function by promoting the formation of myelin, a substance that protects nerve fibers.
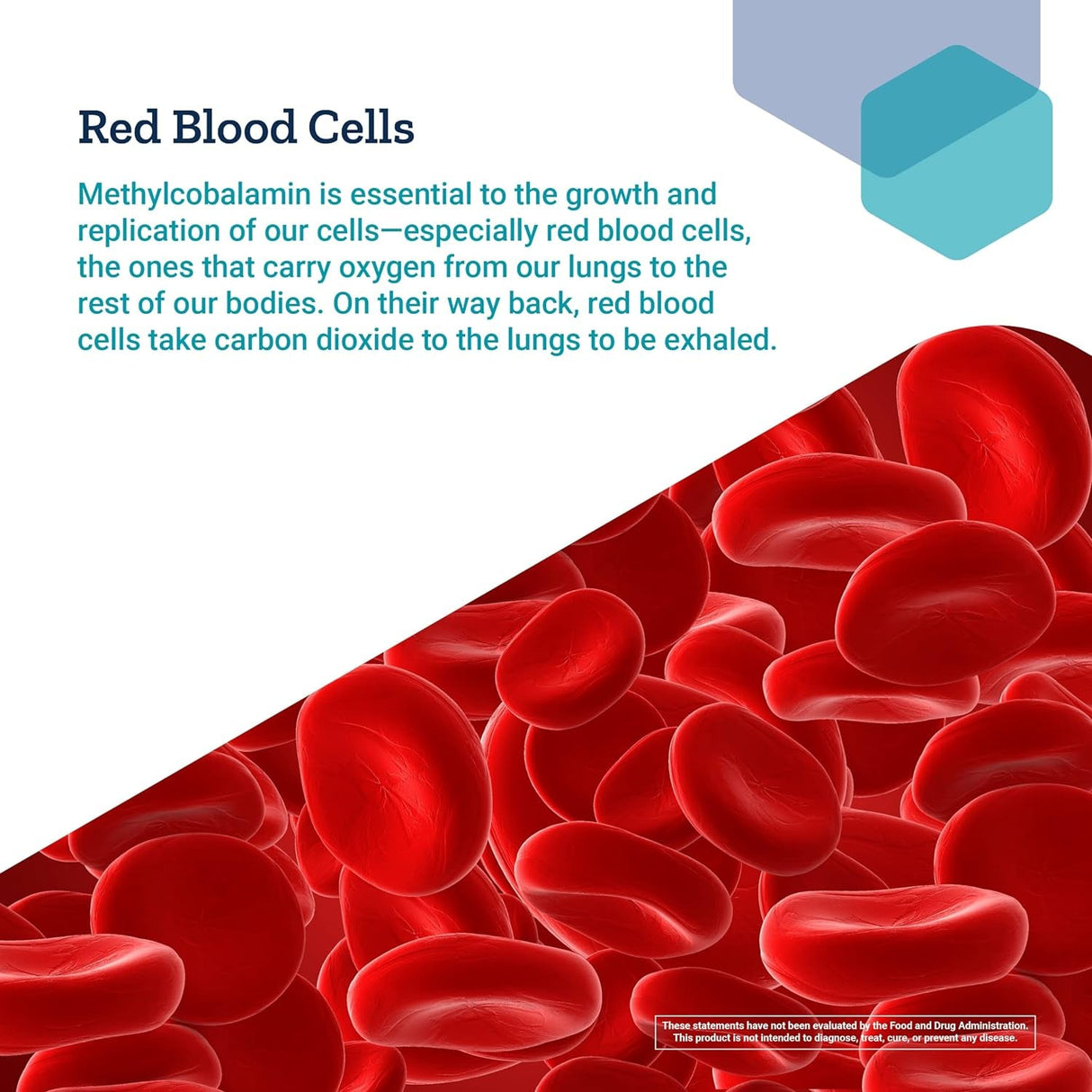
- Blood cell production: Essential for red blood cell production and prevention of B12 deficiency anemia.
- DNA synthesis: Important for healthy growth and repair of cells through DNA production.
- Homocysteine balance: Helps maintain healthy homocysteine levels, which are a marker of good heart health.
- Easily absorbable form: Methylcobalamin is the bioactive form of B12, which means the body can use it directly without the need for conversion.
Technical details and specifications
- Portion size: 1 vegetable melting tablet
-
Amount per serving:
- Vitamin B12 (as methylcobalamin): 1 mg
- Other ingredients: Xylitol, sorbitol, maltodextrin, stearic acid, vegetable stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, natural vanilla flavor, rice flour, modified food starch.
- Quality: Non-GMO, vegetarian formula.
Dosage and use
Dissolve one orodispersible tablet in the mouth or chew daily, as recommended by a healthcare professional. The product can be taken with or without food.
Disclaimer and disclaimer
Allowed to be used by adults over 18 years of age. All use of supplements is at your own risk and should be done in consultation with a doctor. The recommended daily dose should not be exceeded. Dietary supplements should not replace a varied diet. Keep out of the reach of children. Uno Vita AS does not claim that the products we market can cure disease.
Uno Vita increasingly uses artificial intelligence for analysis and design of articles. We do not take responsibility for possible errors in texts or descriptions due to human or computer technology errors. The information is intended as general information and not as a substitute for professional medical advice.
Scientific references
- Green R. et al. "Vitamin B12 deficiency." Nature Reviews Disease Primers, 2017.
- Hunt A. et al. "Vitamin B12 deficiency." BMJ, 2014.
- O'Leary F. et al. "Vitamin B12 in health and disease." Nutrition Reviews, 2010.
- Stacks SP. "Vitamin B12 deficiency." New England Journal of Medicine, 2013.
- Clarke R. et al. "Homocysteine and B vitamins in cardiovascular disease." Journal of the American Heart Association, 2017.
- Yetley EA. et al. "Vitamin B12 status in the US population." American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 2011.
- Good HW. et al. "Vitamin B12 deficiency in the elderly." Annual Review of Nutrition, 1999.
- Andres E. et al. "Vitamin B12 (cobalamin) deficiency in elderly patients." Canadian Medical Association Journal, 2004.
- Allen LH. "How common is vitamin B-12 deficiency?" American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 2009.
- Carmel R. "Subclinical cobalamin deficiency." Annals of Internal Medicine, 1996.
- Mills JL. et al. "Homocysteine and neural tube defects." Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 1998.
- Smith AD. et al. "Homocysteine-lowering by B vitamins slows brain atrophy in mild cognitive impairment." PLoS ONE, 2010.