Omega 3 Algae A+E®
Omega 3 Algae A+E® Black is backordered and will ship as soon as it is back in stock.
Omega-3 Algae A+E®
Summary
Omega-3 Alge A+E® is a plant-based dietary supplement that provides a balanced source of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, combined with fat-soluble vitamins A and E. This product is a sustainable alternative to fish oil and is perfect for vegans, people with fish allergies or those who want an environmentally friendly omega-3 supplement.
Benefits and effects
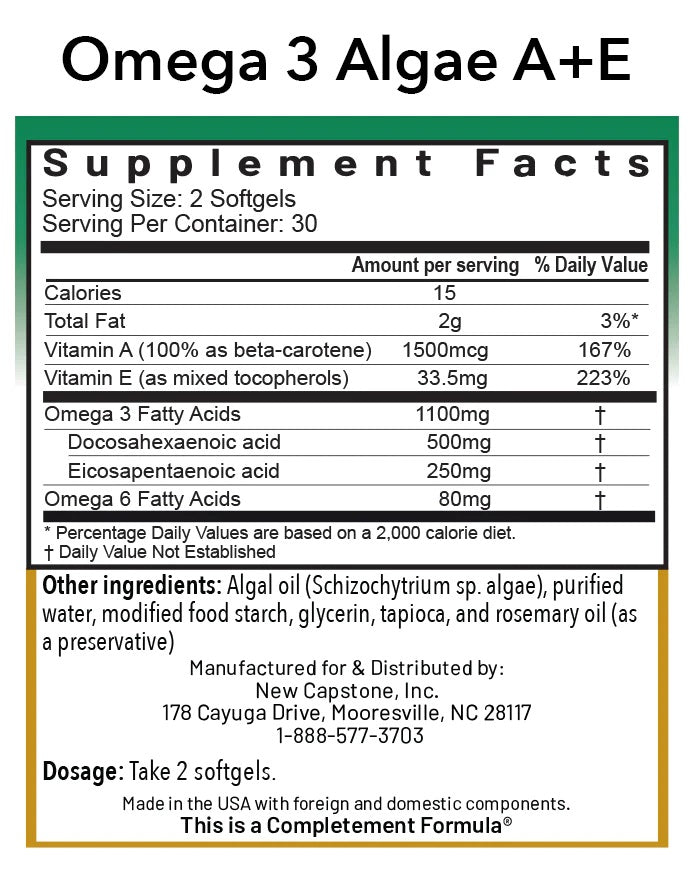
- Vegan-friendly source of essential fatty acids: Omega-3 Alge A+E® contains DHA (500 mg) and EPA (250 mg), which contribute to brain, heart and eye health.
- Vitamin A as beta-carotene: Supports the immune system, vision and skin health.
- Vitamin E as mixed tocopherols: A powerful antioxidant that helps protect cells from oxidative stress.
- Free of fish origin: No regurgitation or discomfort often associated with fish oil.
- Sustainable production: Extracted from algae, which preserves fish stocks and protects marine ecosystems.
Technical details and specifications
-
Ingredients per dose (2 capsules):
- DHA (docosahexaenoic acid): 500 mg
- EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid): 250 mg
- Vitamin A (as beta-carotene): 1500 mcg
- Vitamin E (as mixed tocopherols): 50 IU
- Production: Made in state-of-the-art facilities in the USA under strict quality standards.
- Format: Soft capsules that are easy to swallow.
- Suitable for: Vegans, people with fish allergies and those who want an environmentally friendly alternative.
Recommended use
Take two soft capsules daily, with or without food. This ensures sufficient intake of omega-3 fatty acids and vitamins A and E for daily support for your health.
Disclaimer and disclaimer
- Keep out of reach of children.
- Do not exceed the recommended dose.
- Dietary supplements should not replace a varied diet.
- Uno Vita AS does not claim that this product can cure disease.
- The effect of this product may vary from person to person.
- If you are pregnant, nursing or have a medical condition, consult a doctor before use.
References
- Calder, P. C. (2017). Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and inflammatory processes: Nutrition or pharmacology? British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology.
- Swanson, D., Block, R., & Mousa, S.A. (2012). Omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA: Health benefits throughout life. Advances in Nutrition.
- Mozaffarian, D., & Wu, J.H. (2011). Omega-3 fatty acids and cardiovascular disease: Effects on risk factors, molecular pathways, and clinical events. Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
- Freeman, M.P. et al. (2006). Omega-3 fatty acids: Evidence basis for treatment and future research in psychiatry. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
- Innis, S. M. (2007). Dietary omega-3 fatty acids and the developing brain. Brain Research.
- Simopoulos, A.P. (2002). Omega-3 fatty acids in inflammation and autoimmune diseases. Journal of the American College of Nutrition.
- Rondanelli, M. et al. (2017). Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in the treatment of depressive disorders: An overview. International Journal of Molecular Sciences.
- Fetterman, J.W., & Zdanowicz, M.M. (2009). Therapeutic potential of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in disease. American Journal of Health-System Pharmacy.
- Wang, C. et al. (2006). n-3 fatty acids from fish or fish-oil supplements, but not alpha-linolenic acid, benefit cardiovascular disease outcomes in primary- and secondary-prevention studies: A systematic review. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.
- Ruxton, C.H. et al. (2004). The impact of long-chain n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on human health. Nutrition Research Reviews.
- Kris-Etherton, P.M. et al. (2002). Fish consumption, fish oil, omega-3 fatty acids, and cardiovascular disease. Circulation.
- Harris, W. S., & Von Schacky, C. (2004). The Omega-3 Index: A new risk factor for death from coronary heart disease? Preventive Medicine.