Micellized Pure PC
Micellized Pure PC Black is backordered and will ship as soon as it is back in stock.
Micellarized Pure PC® – Advanced liposomal support for cells, brain and liver
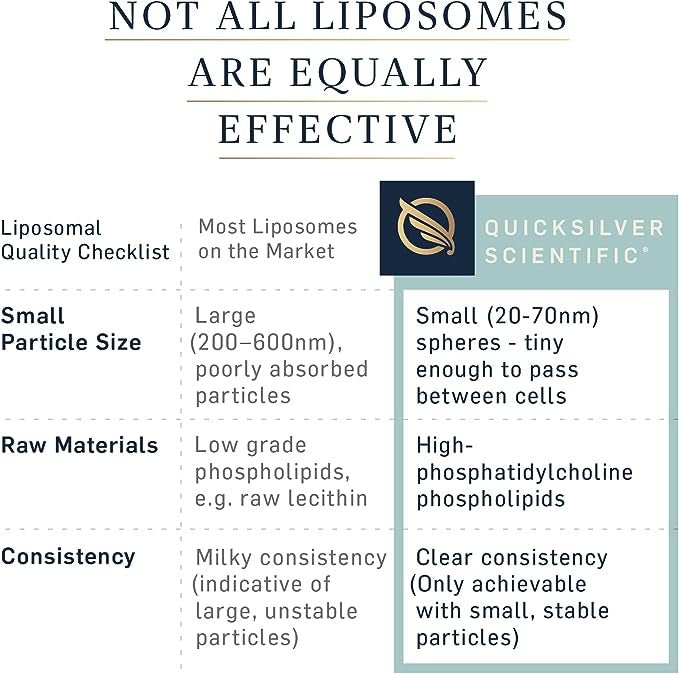
Micellarized Pure PC® is an advanced dietary supplement developed with Quicksilver Scientific's patented liposomal delivery system. The product is formulated to deliver highly purified phosphatidylcholine (PC) in small, stable micelles (20–100 nanometers) that are already absorbed in the oral cavity. This ensures rapid uptake and high bioavailability. Phosphatidylcholine is a key component in cell membranes, nerve tissue and liver cells, and plays a central role in the body's energy metabolism, detoxification and cognitive functions.
Health effects
• Cognitive function: Phosphatidylcholine is a precursor to the neurotransmitter acetylcholine and forms part of the myelin sheath that protects nerve cells. Thus, PC can contribute to memory, focus and mental clarity.
• Cellular health: PC helps to maintain healthy cell membranes and renew membrane structures, which strengthens the cells' resilience.
• Liver support: PC is a building block in liver cells and contributes to normal bile flow and detoxification processes.
• Cholesterol and fat metabolism: PC acts as an emulsifier in fat metabolism and contributes to the transport and excretion of fats.
• Antioxidant and inflammation support: Phosphatidylcholine can help protect against oxidative stress and support the body's natural inflammation regulation.
• Immune balance: PC is included in processes that support the normal function of the immune system.
Top health effects and surprising benefit
• Cognitive support 🧠: PC can help promote memory and focus through its role in acetylcholine production.
• Liver health 💧: PC supports the liver's detoxification and the movement of bile, which is central to the body's natural cleansing processes.
• Surprising advantage ✨: PC has a role in fat transport and can thus contribute to balance in cholesterol levels, an effect that is often not as well known.
Technical details and grant facts
Delivery form: Liposomal liquid with micellization for optimal absorption.
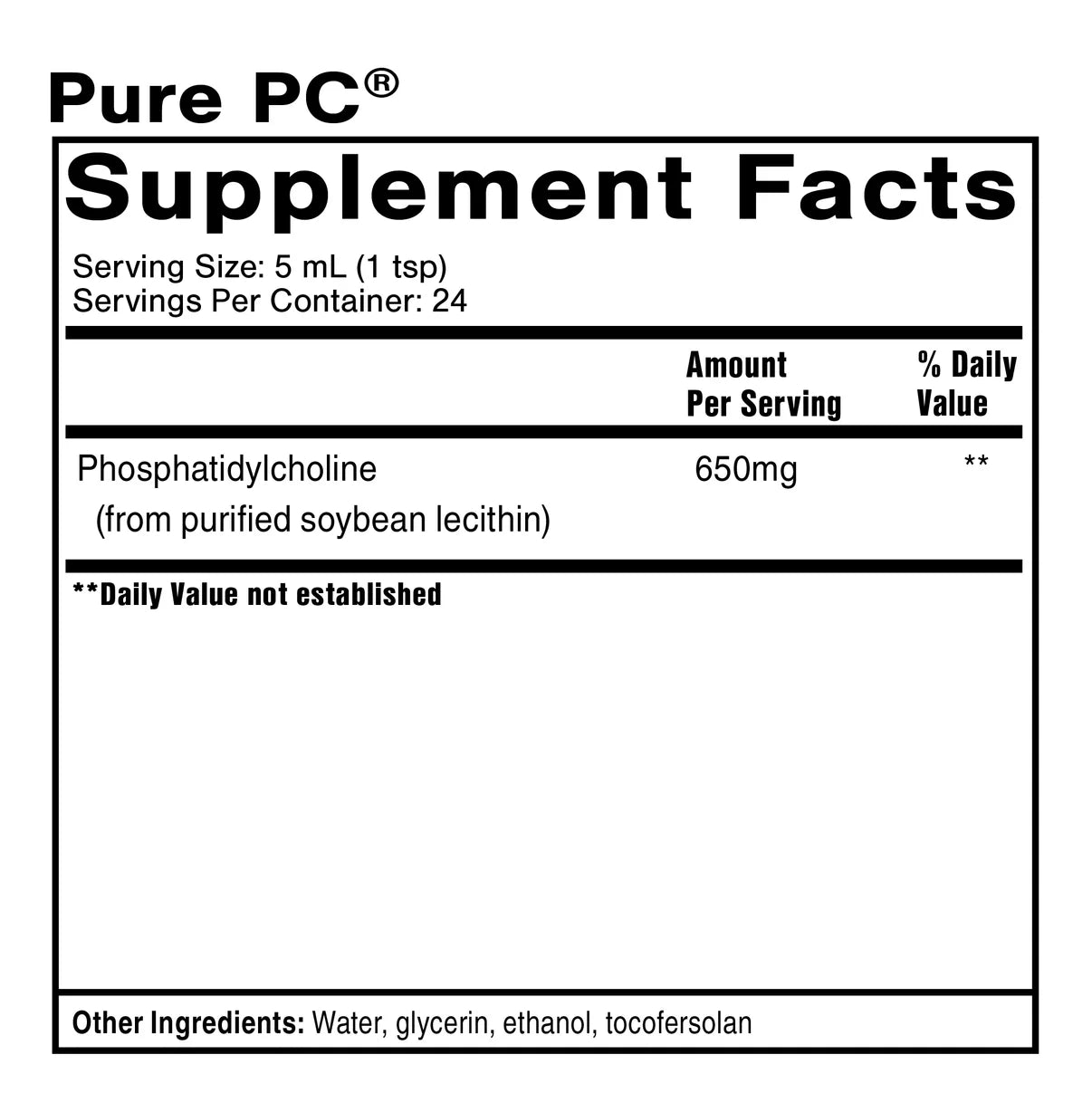
Serving size: 5 ml (1 teaspoon).
Content per portion:
• Phosphatidylcholine (from purified soy lecithin): 650 mg
Other ingredients: Water, glycerin, ethanol, vitamin E (d-alpha tocopherol polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate and natural mixed tocopherols).
Recommended use: 1 teaspoon orally twice daily. Hold in mouth for 30-90 seconds before swallowing. Use on an empty stomach at least 10 minutes before a meal. Store cool and use within 60 days of opening. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should consult a doctor.
Allergens: Contains soy (lecithin). Free from gluten and GMOs.
Storage: Store in a refrigerator after opening. Keep out of the reach of children.
Reservation
Allowed to be used by adults. All use of supplements is at your own risk and should be done in consultation with a doctor. The recommended daily dose should not be exceeded. The effect of this product may vary from person to person. Dietary supplements should not replace a varied diet. Should be kept out of the reach of children. Uno Vita AS does not claim that the products we market can cure disease.
Disclaimer
Uno Vita increasingly uses artificial intelligence for analyses, summaries and design of articles. We do not accept responsibility for possible errors in texts, articles or descriptions due to human or computer technology (AI) errors, inaccuracies or missing information in scientific and medical studies. We encourage all readers to examine all information critically to ensure that the content is correct. Uno Vita does not claim medical effects of the products we sell, but we refer to publicly available research in accordance with the right to freedom of expression. The information on this website is for informational purposes only and is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. All use is at your own risk.
Freedom of expression and right to information
Uno Vita reserves the right to share publicly available research and information on health and wellness technologies, natural substances, vitamins and the like, in accordance with:
• UN Universal Declaration of Human Rights (1948) Article 19
• The International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (1966) Article 19
• Section 100 of the Norwegian Constitution
• America's First Amendment
Scientific references
-
van Blitterswijk WJ, Verheij M. “Phosphatidylcholine metabolism and cell membrane integrity.” Biochim Biophys Acta, 2008.
-
Cui Z, Houweling M. “Phosphatidylcholine and cell function.” Biochim Biophys Acta, 2002.
-
Li Z, Vance DE. "Phosphatidylcholine and choline homeostasis." J Lipid Res, 2008.
-
Yao ZM, Vance DE. "Role of phosphatidylcholine in membrane integrity and function." Trends Cell Biol, 1989.
-
DeLong CJ, Shen YJ, Thomas MJ, Cui Z. “Molecular distinction of phosphatidylcholine synthesis pathways.” J Biol Chem, 1999.
-
Garcia MC, et al. “Phosphatidylcholine supplementation and cognitive function.” J Alzheimer's Dis, 2010.
-
Blusztajn JK, et al. “Choline, acetylcholine, and memory.” Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1987.
-
Kidd PM. "Neuroprotective functions of phosphatidylcholine." Altern With Rev, 1996.
-
Zeisel SH. "Nutritional importance of choline for brain development." J Am Coll Nutr, 2004.
-
Cole LK, et al. "Phosphatidylcholine biosynthesis and liver function." Biochim Biophys Acta, 2012.
-
Yao ZM, Vance DE. "Phosphatidylcholine in very low density lipoprotein assembly." J Biol Chem, 1988.
-
Li Z, et al. "Lipid metabolism and liver disease: role of phosphatidylcholine." Hepatology, 2006.
-
Guseva MV, et al. "Phosphatidylcholine in the regulation of inflammation." Inflam Res, 2014.
-
Sherriff JL, et al. "Phosphatidylcholine intake and cholesterol metabolism." Lipids, 2016.
-
Kullenberg D, et al. "Phosphatidylcholine: structure, metabolism, and health effects." Nutr Rev, 2012.
-
Chiu CC, et al. "Phosphatidylcholine and neurodegenerative disorders." Curr Alzheimer Res, 2008.
-
da Costa KA, et al. "Choline metabolism and homocysteine regulation." Am J Clin Nutr, 2006.
-
Cui Z. “Phosphatidylcholine and neuronal signaling.” Prog Lipid Res, 2011.
-
Fagone P, Jackowski S. “Phosphatidylcholine biosynthesis and cell cycle regulation.” Biochim Biophys Acta, 2013.
-
Vance JE. "Phospholipid synthesis and transport in mammalian cells." Traffic, 2015.
-
Zeisel SH, da Costa KA. "Choline: an essential nutrient for public health." Nutr Rev, 2009.